Introduction: The New Frontier of Companionship
To be alone is to be different, to be different is to be alone. This quote from Suzanne Gordon perfectly captures the paradox of modern society. In today's world, where everyone is just a click away, many still feel like islands in a sea of digital noise. Despite the endless pathways that promise connection, loneliness is growing like a weed. Here’s a twist—what if computers, the things we often blame for this disconnect, become the heroes in the story of companionship?
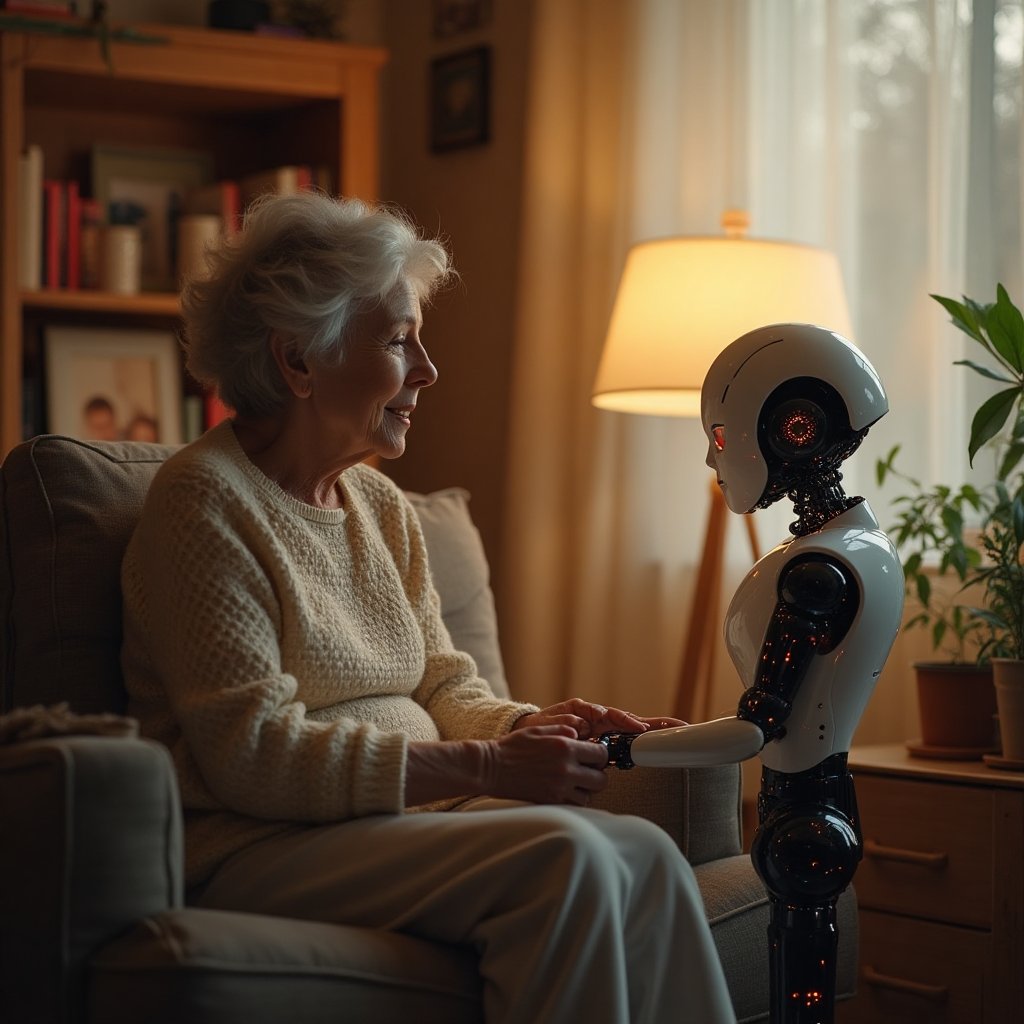
At the heart of this quest for connection is the rise of emotional companion machines. Think R2-D2 with a heart or Wall-E with empathy circuits. These AI-powered friends can talk to us, listen to us, and even understand how we feel. Pioneers like Ray Kurzweil, Sherry Turkle, and Yuval Noah Harari have long mulled over the fusion of humans and technology. They dream of a world where AI isn't just smart but also emotionally in tune. In this exploration, emotional machines aren't just algorithms and wires. They're potential allies that could fight the loneliness epidemic, especially for the elderly or isolated souls who need a miracle in silicon form.
Today, we dive into this brave new world of tech companionship, see how it starts, the science behind it, and its real-life impacts. The story isn't just about machines; it's about understanding, nostalgia, and, most importantly, the quest for human connection.
The Context of Loneliness: Understanding the Epidemic
Loneliness isn't just feeling blue; it's a shadow that wraps around the heart, making the world feel a little colder. This hidden epidemic lingers quietly in the background, touching millions worldwide. The surge in loneliness is unexpectedly connected to the very structures meant to unite us—technology, urbanization, and changing social norms.
The picture of loneliness isn't an unfamiliar face. Recent studies show that in places like the United States, over 30% of the elderly experience loneliness on a regular basis. The UK's Office for National Statistics reports similar concerns, emphasizing that this pandemic of isolation is just as serious as any physical ailment.
And why does this matter? Loneliness isn't just an emotional woe; it comes with physical baggage. Studies from institutions like Harvard link loneliness with increased risks of Alzheimer's, depression, and cardiovascular issues. The mind and body are unexpectedly intertwined, and as social beings, neglecting social needs can lead to startling health setbacks.
Recognizing loneliness as an epidemic isn't just about pointing fingers or finding villains in technology. It's about understanding why we feel the way we do and considering new approaches. Emotional companionship through AI might just be the compass we need in this chaotic map of modern life. They promise more than just data and code; they offer a chance for a more connected future.
The Evolution of Technology: From Robots to Emotional Companions
Technology has always been a pivotal player in the grand tale of companionship's evolution. Remember when a Tamagotchi was the pinnacle of technological friendship? We've come a long way since then! This part of our journey examines how artificial intelligence (AI) transitioned from basic robotics to the sophisticated emotional companions of today.
A Brief History of AI in Social Interactions
AI's history is like that of an awkward teenager growing up and finding its place in the world. It started with simple calculations but slowly morphed into more complex functions, like learning how to dance at the prom. Impressively, it advanced to humanoid robots, which aren’t just about doing the Macarena but actually recognizing emotions and responding to them. This journey is like teaching your dog new tricks, but the dog can now comfort you when you're feeling down. Humor aside, the progression of AI denotes how far technology has come in understanding social cues and providing interaction akin to human relationships.
Case Studies and Current Technologies
Diving into the real world, we see AI applications like Paro the robotic seal offering therapeutic benefits. Paro, despite looking like someone's living room slipper, responds intuitively to touch, mirrors users' emotions, and brings joy to many, especially in therapeutic settings. It's comforting like a soft hug on a chilly evening. Such real-world applications signify AI's burgeoning role in recreating emotional bonds and its promising capability to combat loneliness.
The exploration of these high-tech gadgets underscores our transition from mere functional robotics to emotionally intelligent partners that offer comfort, companionship, and empathy.
Designing Emotional Companions: What Makes Them Effective?
The secret sauce to an effective emotional companion machine isn’t just bolts and code. It’s more like an AI cocktail—equal parts emotion, understanding, and adaptability. These elements transform them from simply being robotic butlers to engaging pals by your side.
Emotion Recognition and Interaction Design
Imagine if your microwave could tell when you're sad about the burnt popcorn. Emotional recognition is fundamental to ECMs and involves sensory and AI developments that can interpret intricate human emotions. Modern ECMs, equipped with sensors and advanced machine learning algorithms, are masters at catching emotional cues. Think of them as therapists with silicon hearts, understanding emotions from our speech, facial gestures, or even our swift intake of breath when we’re startled. These machines are built to sense, respond emotionally, and recreate human-like interactions seamlessly.
Personalization and Adaptability
If humans are snowflakes, ECMs are like those magical snow blowers that craft unique, delicate snowflakes for each person. Personalization is critical, and machines today are adept at learning preferences over time. If you love jazz, your ECM might play Miles Davis when you’re brooding, offering that distinctive soundtrack tailored to your mood. Such adaptive responses turn otherwise monotonous interactions into vibrant, personalized experiences, akin to having your very own DJ and life-coach rolled into one nifty machine.
Delving into these design principles demystifies how emotional companions stand apart from their robotic relatives, capable of significantly enhancing the well-being of those they accompany.
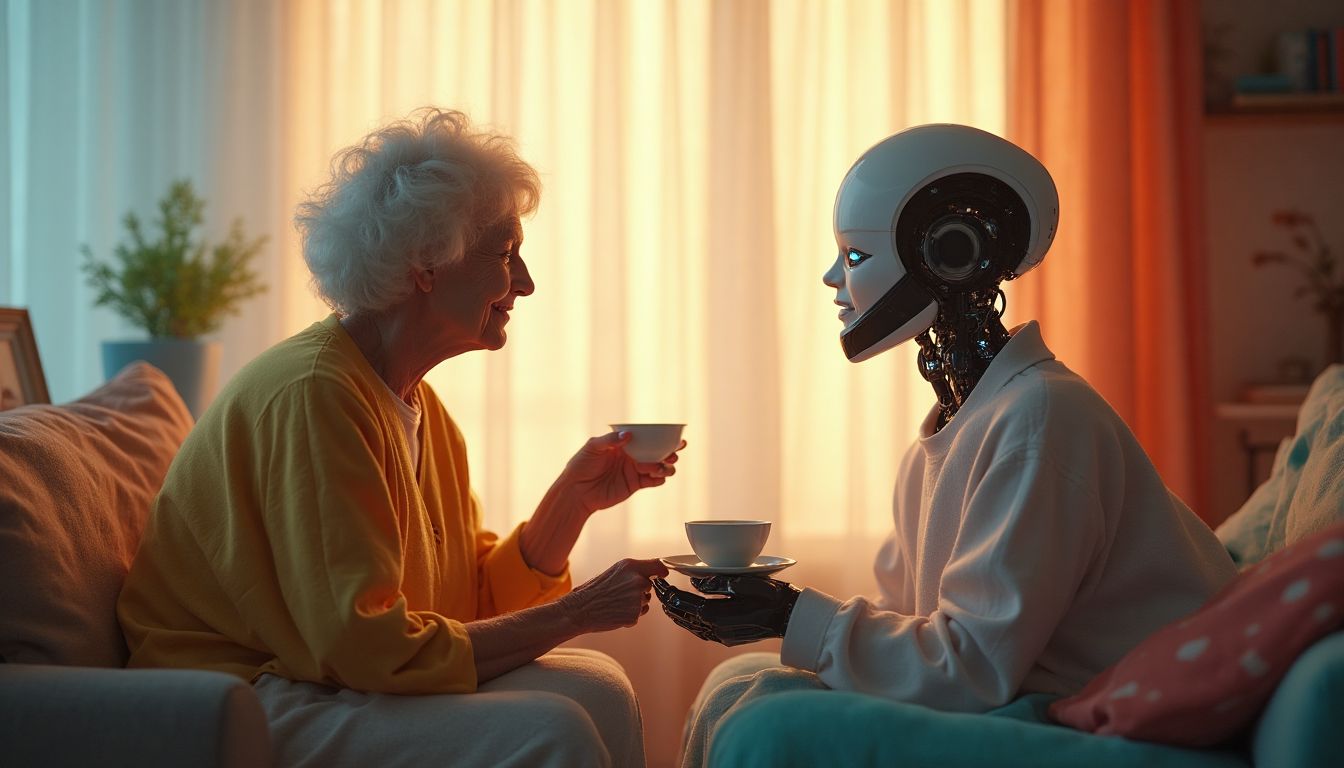
4. Real-World Applications: The Impact of AI Companions on Loneliness
When it comes to transforming lives, AI companions are not just a thing of science fiction; they are here, driving change with real-world applications. These empathetic machines are rooted in today's actionable reality, helping combat loneliness for individuals across the globe. But exactly how effective are they?
4.1 Reviews and Success Stories
Take EliQ, a friendly robot known for its conversational skills, as a prime example. Reviews from satisfied users have surfaced, showcasing EliQ's ability to engage in meaningful dialogues, often providing comfort and reducing stress among older users. A recent article by The Guardian highlights stories where these machines have significantly improved mental well-being.
Additionally, Buddy, another AI therapist from Blue Frog Robotics, actively encourages social engagement by organizing games and activities. A CNN report on Buddy illustrates its role in bringing joy and reducing feelings of solitude, especially among the elderly.
4.2 Limitations and Challenges
Despite glowing reviews, challenges loom large. The hurdles of trust cannot be overlooked. Can machines adequately replace human touch, or are these just empty gestures? Furthermore, there is the quandary of ensuring the authenticity of interactions. Are we genuinely being heard, or is it merely programmed empathy?
Additionally, socio-economic barriers pose a dilemma, as not everyone can access the benefits of AI companions. The
Pew Research Center
outlines digital divides and the disparity in technology adoption, primarily in less affluent sectors.
Understanding both achievements and setbacks brings a well-rounded perspective to the transformative role AI can serve in alleviating the pain of loneliness across diverse communities.
5. Future Directions: The Next Frontier of Emotional Companionship
The future holds immense possibilities for emotional companions, with emerging innovations striving for precision and effectiveness in mitigating loneliness.
5.1 Technological Advancements and Innovations
Research and development do not stand still; they are the ground beneath the moving train of progress. Imagine emotional companions enhanced with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), allowing users to immerse themselves in artificially crafted yet believable environments. As discussed in Wired,
such advancements can provide enriching experiences that go beyond traditional interactions.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Aims to create interactive, immersive environments, where users can engage with digital companions in familiar settings.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Blends real-world scenarios with virtual interactions, enabling companionship models that appear tangibly present.
5.2 Ethical Considerations
Yet, as with all progress, ethical questions arise. What does it mean for human emotions to be mapped so meticulously by machine algorithms? Concerns about emotional dependency are bubbling up, as individuals might lean excessively on machines, blurring the line between tool and crutch. Further, privacy concerns around data collection and usage echo across stakeholders.
For a deeper dive into such humanistic concerns,
Harvard
provides a platform for discourse surrounding the moral landscape of AI advancements.
With each stride toward a future where technology and humanity walk hand-in-hand, examining these facets will ensure we cultivate a promising world where loneliness meets its match.
AI Solutions: A Multi-Faceted Approach to Combatting Loneliness
The potential of AI in tackling loneliness goes beyond just creating machines that interact; it involves a nuanced and layered strategy to uplift emotional well-being. This approach should utilize human-like empathy, cutting-edge technology, and strong community engagement. Here's a breakdown of how AI can effectively address loneliness:
Detecting and Understanding Loneliness
To begin, we need to implement AI surveillance systems that monitor social behavior and emotional cues in real-time. Machine learning algorithms can analyze data collected from social media interactions, online engagement patterns, and even physiological data gathered from wearable technology. These platforms can determine when individuals display signs of loneliness or emotional distress, allowing for timely interventions. This system must respect privacy and be transparent about data use, earning the trust of users.
Personalized Interaction Models
Creating adaptive algorithms for emotional companions that react based on the user’s mood and preferences is essential. AI can library a range of human-like responses using voice modulation to convey empathy. By analyzing past interactions, AI companions can learn to initiate conversations about topics that interest users or even schedule virtual activities like movie watching or book clubs. This level of personalization transforms a basic machine into a genuine source of support. Tools such as Spotify playlists tailored to the individual's taste can merge companionship with entertainment.
Collaborative Human-AI Framework
A successful solution to loneliness requires collaboration between AI systems and human professionals such as psychologists, therapists, and social workers. By integrating human insights, machines can develop a more profound sense of empathy and understanding. This partnership can ensure that vulnerable populations receive holistic support. Institutions like the AARP could advocate for programs that integrate AI technologies into community outreach for elderly care, emphasizing emotional health.
Action Schedule/Roadmap (Day 1 to Year 2)
This roadmap outlines practical steps for creating AI capabilities to combat loneliness effectively:
- Day 1: Assemble a diverse interdisciplinary team of psychologists, AI developers, social workers, and community leaders, fostering a wide-ranging perspective on loneliness. Engage organizations like NAMI (National Alliance on Mental Illness) for insights on mental health.
- Day 2: Establish a mission statement and define the parameters for measuring the impact of AI solutions on reducing loneliness.
- Day 3: Conduct initial interviews with potential users, facilitating discussions to collect qualitative data on personal experiences with loneliness, focusing on diverse demographics.
- Week 1: Complete comprehensive market research on existing technologies aimed at alleviating loneliness to inform the AI’s development.
- Week 2: Develop initial prototypes that utilize emotional analytics for interactive sessions with users. Collaborate with tech companies that focus on AI development, such as IBM Watson.
- Week 3: Introduce user testing, focusing on gathering feedback through controlled trials. Employ iterative processes in design and functionality to refine user interaction.
- Month 1: Launch focus groups where users engage with prototypes over a series of sessions, evaluating their emotional responses and suggest improvements.
- Month 2: Begin the integration of machine learning to personalize responses based on user collected data, enhancing interactivity and engagement.
- Month 3: Host community forums involving stakeholders, caregivers, and researchers. These meetings aim to discuss ethical considerations surrounding AI companionship while ensuring the program aligns with social needs.
- Year 1: Deploy beta testing throughout selected communities, focusing on the elderly and isolated individuals. Gather thorough data on user engagement metrics and emotional health responses.
- Year 1.5: Analyze results, iterating on AI capabilities based on user feedback and emotional engagement metrics collected during testing phases.
- Year 2: Launch the final version of emotional companions to a broader audience, complemented by public awareness campaigns on the benefits and usage of AI in promoting emotional well-being.
Conclusion: A New Era of Companionship
As we stand at the intersection of technology and human emotion, the rise of AI companions represents a tangible step towards addressing loneliness, particularly among vulnerable populations. While challenges persist, including ethical concerns and technological limitations, the potential for emotional companionship extends far beyond alleviating solitude; it echoes a deep-rooted human desire for connection. The question remains: Can AI truly fill the void left by human absence? With continued innovation and a keen focus on fostering meaningful interactions, the answer may soon become a heartwarming "yes."
FAQ: Understanding AI and Emotional Companionship
-
What are emotional companion machines?
Emotional companion machines, or ECMs, are special types of computers and robots designed to help people feel less lonely. They can talk to you, listen to you, and even understand your feelings. These machines use AI technology to create meaningful conversations, and they adapt to what you like and how you feel.
-
Who can benefit from AI companions?
Many people can find comfort in using AI companions. They are especially helpful for:
- Older adults who may feel lonely.
- People who live alone and have few visitors.
- Those going through difficult times, like loss or change.
- Individuals with disabilities who find it hard to interact with others.
-
Are there any risks associated with using AI companions?
While AI companions can help people feel less lonely, there are some risks to think about:
- Emotional dependency: Sometimes, people may become too attached to their AI companions.
- Privacy concerns: Users should be careful about sharing personal information with AI companions.
- Authenticity: Some people might wonder if the feelings expressed by AI are real or just programmed responses.
-
How do AI companions recognize emotions?
AI companions use special tools to understand human emotions. They look at your facial expressions, listen to how you speak, and sometimes even check your heart rate or body language. By evaluating these signals, they can respond appropriately. For more on emotion recognition technology, check out this Wikipedia article on Emotion Recognition.
-
Will AI companions replace human relationships?
No, AI companions are not meant to replace real friendships or family ties. Instead, they are designed to offer support and help fill in the gaps when human interaction is lacking. Think of them as a little extra cheerleader or friend when you need one!
-
How can I find the right emotional companion for me?
Finding the right AI companion can be fun! Here are some tips to help you:
- Check online reviews to see what others say about different companions.
- Consider what features you want–like talking, playing games, or helping with reminders.
- Visit websites that compare different AI companions, like Tech.co's review of robot companions.
-
Are there different types of emotional companions?
Absolutely! There are various types of emotional companions. Some are robots, like Paro, a cute robotic seal that interacts through touch and sound. Others are software-based applications on phones or tablets that you can chat with, like Replika. Each type has unique features, so you can choose one that fits your needs.
Wait! There's more...check out our gripping short story that continues the journey: The Architects of Tomorrow
Disclaimer: This article may contain affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, we may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. Our recommendations and reviews are always independent and objective, aiming to provide you with the best information and resources.
Get Exclusive Stories, Photos, Art & Offers - Subscribe Today!




























Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.